Diabetic Retinopathy
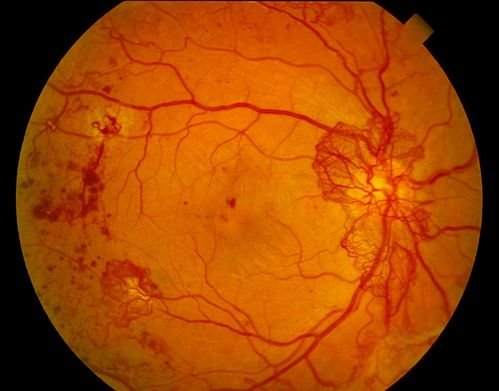 Despite advancements is the management of diabetes including early diagnosis, prompt treatment and eye screening, diabetic retinopathy remains a common condition requiring active intervention with laser and surgery.
Despite advancements is the management of diabetes including early diagnosis, prompt treatment and eye screening, diabetic retinopathy remains a common condition requiring active intervention with laser and surgery.
How does diabetes affect the eye?
Diabetes primarily affects the back of the eye (retina) by occluding its blood circulation and impairing the transport of nutrients. It can affect the vision in a number of ways.
Macular Oedema – leakage of fluid under the central and most sensitive part of the retina resulting in variable loss of central vision, which typically affects reading.
Neovascularisation (new blood vessels) – lack of circulation stimulates formation of a special agent called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) which in turn causes proliferation of abnormal new blood vessels on the retina. These vessels are fragile and prone to rupture resulting in leaking of blood in the vitreous. Consequently resulting in a sudden loss of vision. Moreover, abnormal blood vessels result in the formation of fibrous scar tissue/membranes on the retina, causing it to detach and obscure vision.
Retinal Ischaemia (lack of circulation) – closing down of retinal vessels in itself can cause loss of vision.
Cataract – diabetic individuals are at a high risk of developing cataract at a relatively young age.
Nerve Palsy – Interruption to the blood flow to the nerves controlling eye muscles can result in sudden onset of double vision. It is usually self limiting. Prompt referral to your Ophthalmologist is required
What is the treatment of diabetic retinopathy?
Several advancements have been made in the recent years to improve the outcome of vision in diabetic eye disease.
Laser Photocoagulation – This is a well established treatment modality to treat new vessels, thereby reducing the risk of haemorrhage. It reduces the risk of severe loss of vision by 50%. Laser is also used to treat macular oedema. The treatment is carried out as an outpatient or a day case under local anaesthesia with minimal discomfort.
Anti-VEGF – This relatively new class of drug has shown good results in resolving macular oedema. The treatment entails serial injections of a tiny amount of drugs such as LUCENTIS or EYLEA into the eye.
Steroids – OZURDEX implant is a very effective treatment for diabetic macular oedema. Its effect is much longer lasting than anti-VEGF.
Vitrectomy – Vitreous haemorrhage, retinal membranes or detachment can be removed with the most modern state of the art vitrectomy, and microsurgical suture-less techniques. The outlook of severe diabetic eye disease has been transformed with vitrectomy surgery.
The procedure is carried out under local anaesthesia on a day-case basis and takes approximately 1-2 hours depending on the complexity of your eye condition.
Often a combination of the above mentioned treatments is used to achieve optimum result and to customize treatment according to individual circumstances.